Telehealth Services Available 24/7
See a doctor within minutes and get an Rx from any local pharmacy.

Available in 50 states. Insurance accepted.
Fast
virtual visits
24/7 care
assistants
Prescriptions
as needed
As seen in

Comprehensive care, where you are
Access a wide range of essential healthcare services tailored to your needs, all from the comfort of your home
See If Delivery Is Available Near You
Delivery Not Available
Enter your ZIP code to check if prescription delivery is available in your area and how soon your meds could arrive.
How to get started
Choose your doctor, start a virtual visit, and have your prescriptions sent to your preferred pharmacy for pickup — all in just a few easy steps.
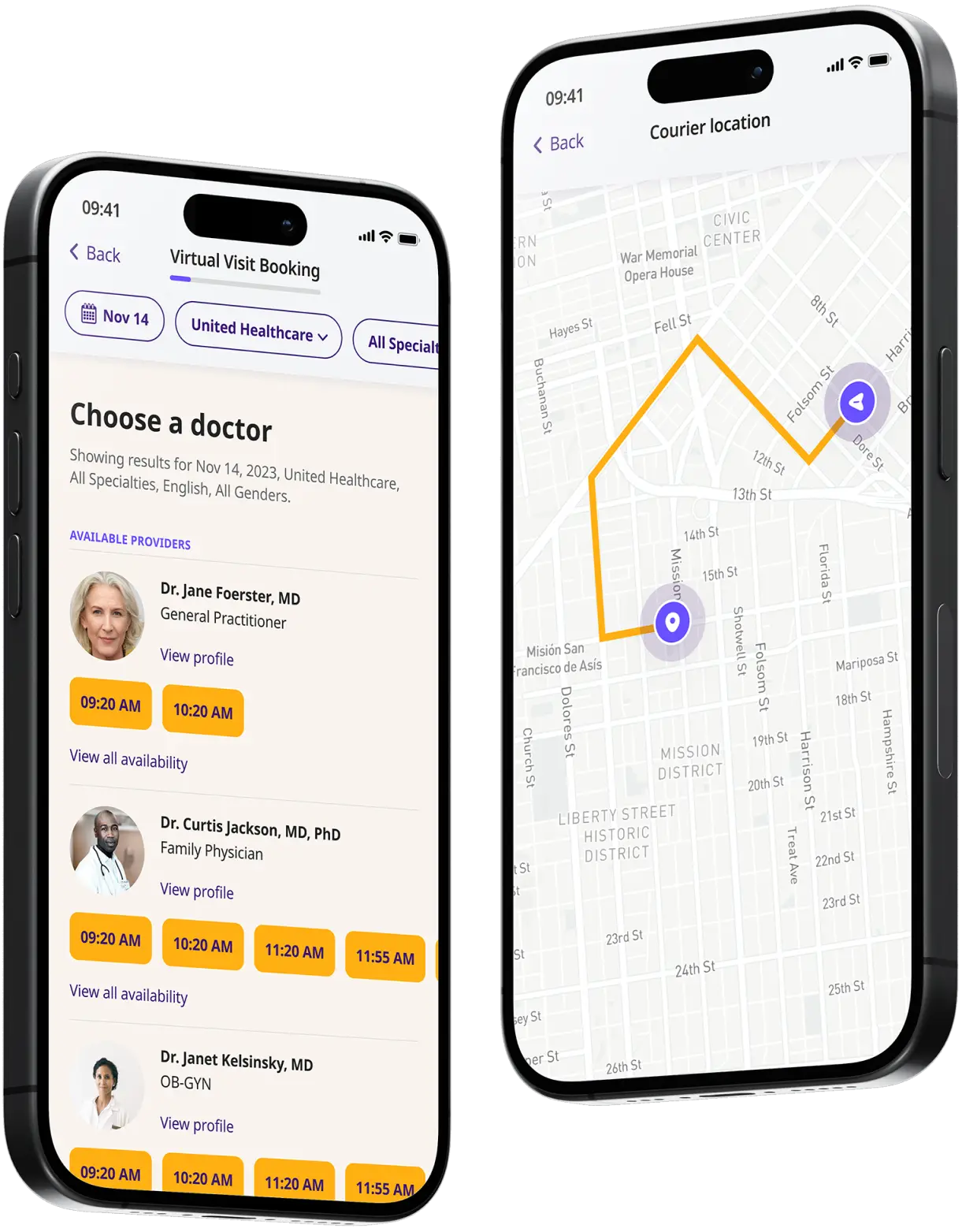
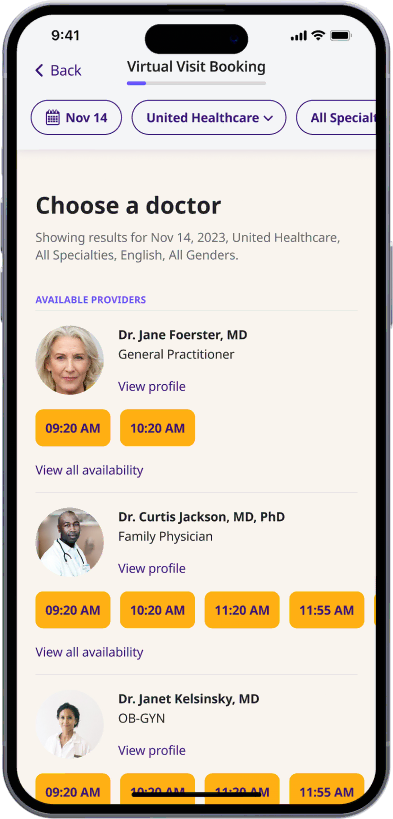
Choose a doctor
Choose a physician by availability, specialty, ratings, and more.
Start a video call
Get connected with a doctor anytime, anywhere.

1-Hour Rx Delivery
Your prescription delivered to your door in 1 hour or less.
Available in 50 states. Insurance accepted.
One-Time
Physician Visit
One-time visit with a physician for diagnosis, treatment, Rx, labs, referrals, and doctor’s notes.
Accepted Insurances